Case Study: Nanopath’s Implementation of Additive Manufacturing
Advancing Medical Diagnostics with Cutting-Edge Manufacturing
The use of cutting-edge advanced manufacturing techniques has the potential to dramatically accelerate the commercialization of high-impact medical diagnostics and devices—while ensuring patient safety and compliance with quality regulations.
Advanced manufacturing is an umbrella term for innovatively applied medical product manufacturing technologies that improve quality, address supply shortages, and speed time-to-market. These tools include 3D printing/additive manufacturing, artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML), enterprise resource planning (ERP), product lifecycle management (PLM), quality management systems (QMS), robotics, cloud computing, digital twins, digital threads, and IoT-enabled solutions.
Looking ahead, these technologies are reshaping the medical device industry by improving efficiency, reducing development costs and timelines, and ultimately leading to better patient outcomes. Through collaboration with MDIC’s Advanced Manufacturing Clearing House, Nanopath has begun implementing advanced manufacturing across its in vitro diagnostic (IVD) platform—from design and fabrication to analysis—to accelerate development, optimize manufacturing, and scale its innovative nanobiosensor technology for women’s health. More case studies from their collaboration with MDIC can be found at MDIC.org/amch.
Nanopath's Digital Transformation At-a-Glance
Nanopath’s platform harnesses the potential of an untapped biosensing modality to sensitively and specifically detect viral, bacterial, and fungal pathogens without the need for nucleic acid amplification, dramatically decreasing time-to-result. Nanopath leveraged microspotting, a specialized form of additive manufacturing, to fabricate its proprietary nanobiosensors. By transitioning from manual and semi-automated methods to industrial-scale precision micro-deposition, the company achieved:
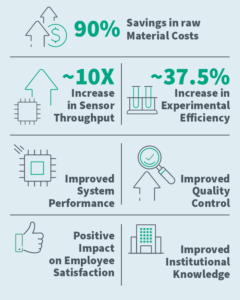 90% Savings in Raw Material Costs
90% Savings in Raw Material Costs
Reduced reagent volumes from 20 µL to 2 µL per sensing spot with industrial-scale microspotting.- 37.5% Increase in Experimental Efficiency
Smaller spot sizes allowed more replicates per slide, streamlining assay optimization. - 10x Increase in Sensor Fabrication Throughput
Automated microspotting produced hundreds of spots per hour, boosting yield and efficiency. - Improved Sensor & Assay Performance
Precise tuning of droplet size and array layout enhanced integration and overall performance. - Improved Quality Control (QC)
Real-time imaging and automated deposition reduced variability and identified faulty reagents early. - Improved Institutional Knowledge
High-throughput micro-deposition built expertise for broader applications in diagnostics and beyond - Positive Impact in Employee Satisfaction
Automation reduced repetitive tasks, improved morale, and accelerated progress toward commercialization.
Supporting Regulatory Confidence
Advanced manufacturing strengthens compliance efforts by improving data accuracy and product reliability. Nanopath anticipates that additive manufacturing will support faster FDA review processes and lower regulatory costs by ensuring robust, high-quality data.
About Nanopath
Nanopath is an early-stage molecular diagnostics company working to bridge the women’s healthcare gap through the development and commercialization of a state-of-the-art platform for rapid, point-of-care diagnosis of pelvic and gynecologic infections. Nanopath is a company founded by women for women. The company’s co-founders, Dr. Alison Burklund and Dr. Amogha Tadimety, developed the core technology platform during their tenure as Ph.D. researchers at Dartmouth College, where they were fellows in the prestigious Ph.D. Innovation Program. The pair shared a vision of moving novel technology from bench to market and are dedicated to equitably improving health worldwide. Nanopath is headquartered in Cambridge, MA at The Engine built by Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) – a premier and selective launchpad for “tough tech” start-ups. Nanopath currently employs 17 full-time employees and has raised over $21M in a combination of venture capital and federal funding (NIH, NSF). Nanopath also has active clinical partnerships through approved institutional review boards (IRBs) with Mass General Brigham (Boston, MA) and Dartmouth Health (Lebanon, NH).